Objectives
Not a day goes by without a news report or opinion piece published involving a case like the MeToo Movement, spycams, university SNS sexual harassment, or the Nth Room scandal. As the need for gender sensitivity becomes more and more apparent, interest in sexuality, anger over sexually based crimes, and solidarity with victims is becoming stronger. However, it remains common for people and the media, to confuse and misuse words such as sexual harassment, sexual assault and sexual abuse. Healthy and helpful criticism can only occur with a clear understanding through an accurate comprehension of key concepts.
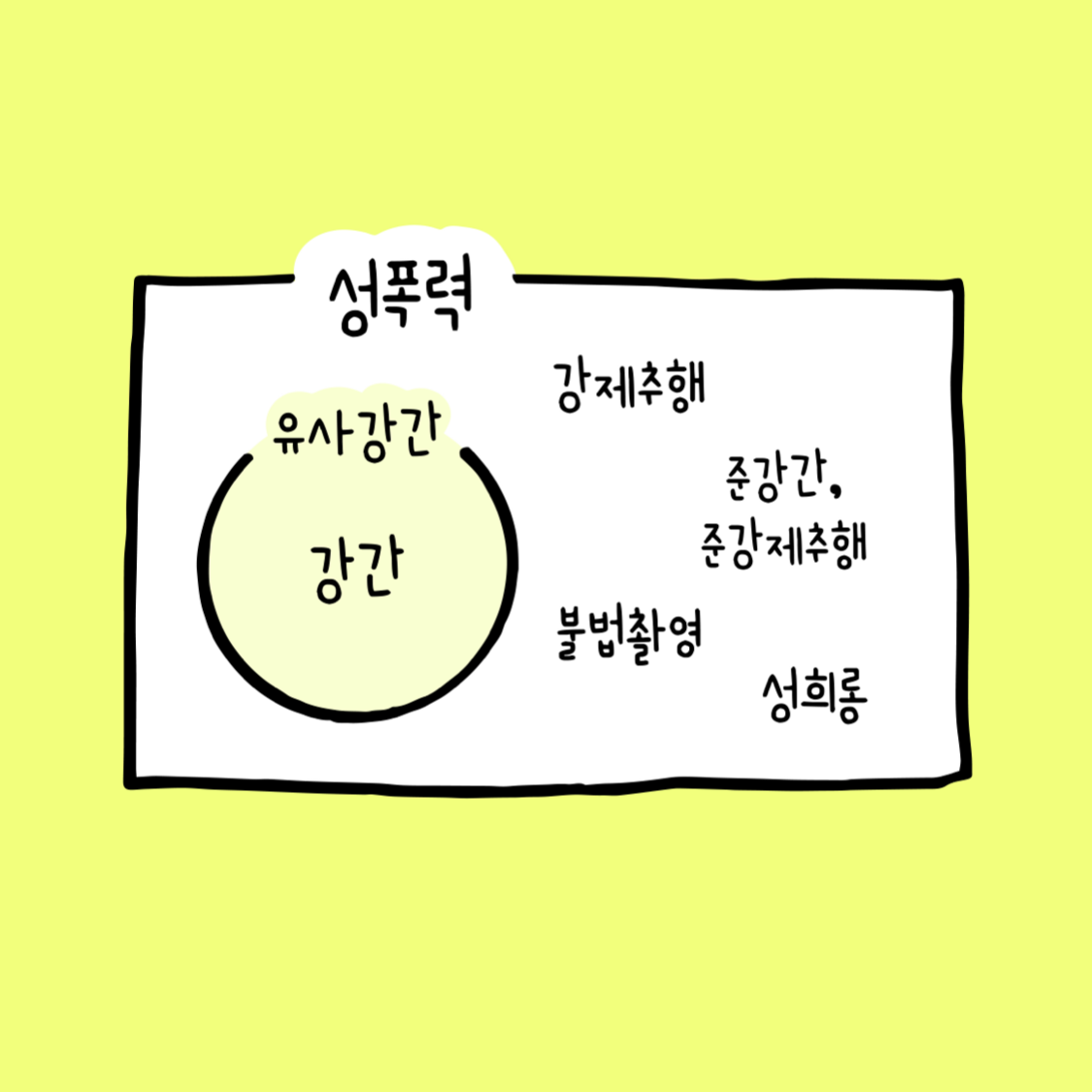
🔍‘Sexual Violence’ A closer look
What does it mean?

- Sexual violence related laws do not only include criminal offences like rape and sexual assault, but also civil disputes in some cases of sexual harassment.
- Not all forms of sexual violence can be trialled in a criminal court, but that doesn’t mean that the act itself is not sexual violence.
Forms of Sexual Violence
It would be near impossible to classify all the forms of sexual crimes. And various factors such as the victims characteristics or environment, the perpetrators social status, and the relationship between the parties should all be considered. Nevertheless, the representative forms of sexual violence are presented below.
- Sexual Assault
Also referred to as indecent assault, this regards any offensive act involving touching or threatening someone sexually without their consent.
This crime can be established regardless of whether the perpetrators motivations were innately sexual. Many of the cases we think of as criminal sexual violence fall under this category.
- Rape
Penetrative intercourse carried out without the victims consent is considered rape. In many countries this includes penetration of the vagina, anus, or mouth by a penis, finger, or other object. Some countries laws differentiate criminal classifications based on the orifice penetrated or the object/appendage used to penetrate.
- Sexual Assault of a Minor
Any sexual activity conducted with a minor under the age of consent, regardless of the use of violence or threats, is also considered sexual assault. Even if the minor was a willing participant in the act they are not considered mentally or emotionally capable of giving consent. This is sometimes called ‘statutory rape’. Different countries around the world recognise different ages of consent, complete with various exceptions.
- Sexual Assault of Someone Impaired or Incapacitated
Even without violence or threats, if the victim is mentally or physically impaired or incapacitated, they are not considered capable of giving consent to sexual activity.
- Forcible Touching
This can include the intentional rubbing up against or the touching of a non-consenting person for the purpose of sexual gratification. This is often in public places such as on trains or buses where the victim may not be aware of what is happening, or be able to stop it.
- Sexual Harassment
The use of explicit or implicit sexual overtones that are unwelcome or inappropriate. This harassment could include sexual advances, requests for sexual favours, or negative comments about women as a group. It can also include penalizing a victim for not complying with sexual requests, and can be established even if the victim does not explicitly state their discomfort or refusal.
- Stalking
A pattern of behavior directed at a specific person that would cause a reasonable person to feel fear. This can include following the victim in person, monitoring them, repeatedly sending unwanted messages or gifts, and approaching friends or family.
- Voyeurism/Indecent Exposure
Voyeurism involves the act of trespassing or otherwise invading the privacy of another to spy or eavesdrop for the purpose of sexual arousal, while indecent exposure is the deliberate and unsolicited exposure of ones own genitals or sex acts to an unwilling audience. This is sometimes also known as ‘flashing’.
- Sexual Exploitation and Abuse
Sexual abuse is the use of a position of power, authority or trust to sexually assault a victim, while sexual exploitation specifies profiting monetarily, socially, or politically, from the sexual abuse of another. Sexual abuse can occur within an environment that should be safe for the victim, such as at home, school or a religious center.
- Sex Trafficking
Sex trafficking is a crime that occurs when an individual is forced, tricked or coerced to be involved in commercial sexual acts, and can include being sold or transported overseas. Perpetrators often target people who are poor, vulnerable, living in an unsafe situation, or searching for a better life.
- Intimate Partner Violence
Includes any kind of abuse or aggression occurring within a romantic relationship. Abuse can be sexual, physical, emotional, financial and/or reproductive. It can also occur between two individuals after separation.
- Cyber-Based Sex Crimes
Sex crimes conducted over the internet can often be harder to categorize, prove and punish.
- Harassment/Stalking
Can involve sending unwanted or offensive pictures, articles, videos, messages or threats of a physical or sexual nature. Can also involve gender-based bullying through trolling, harassment, and cybersexism playing on gender-based power structures.
- Illegal Filming and/or Distribution (spycams/revenge porn)
Taking a picture or video of an individuals body regardless of their will as well as distributing, selling, or displaying the material with others. This can include the non-consensual sharing of material that was made consensually with the perpetrator, such as so called ‘revenge porn’.
Concept Review ⭕️❌ QUIZ!
🙅♀️ Regardless of gender, anyone can be a victim of rape.
🙅♀️ Sexual harassment can be established regardless of the perpetrators motives.
🙆♀️ Online bullying on the basis of someone’s gender can also be considered sexual violence, causing fear and distress in victims through targeted attacks.
Summary
- Sexual violence includes assault, harassment, exploitation and cyber-based crimes.
- Judgement should be based not on the perpetrators standards but the victims.
- Sexual Violence is always the perpetrators fault, not the victims. Listen to victims stories.